LB is generally interpreted as Luria -Bertani, but according to its inventor Giuseppe Bertani, the name comes from English Lysogeny broth, that is, lysozyme broth. In recent years, LB culture media is used as one of the commonly meida used for bacterial growth and recipient bacterial(escherichia coli).
LB culture media is one of the most widely used media used for bacteria growth, sometimes called common media, containing yeast extract, tryptone and NaCl。
Yeast extract: a light yellow powder rich in small molecules of amino acids, peptides, nucleotides, vitamins and other natural active ingredients extracted by yeast after breaking the wall, and then hydrolyzed by biological enzyme, in which amino acids content more than 30%, more than 50% of the total protein and more than 10% of the nucleotide are widely used as raw materials for the production of biological culture media and food seasoning.
Tryptone: a high-quality peptone. It is a white powder made from fresh beef and beef bone digested by trypsin and concentrated and dried. It is rich in nitrogen sources, amino acids, etc.
Yeast extract provides microorganism with carbon source, energy, phosphate, growth factor, vitamin, etc; peptone mainly provides nitrogen source; NaCl mainly provides microbial growth environment (such as osmotic pressure), then it also provides inorganic salt.
A certain amount of agar should be added as coagulant when preparing solid media. Agar at normal concentration will dissolve at 96 ℃. In general, it dissolves in boiling water bath or asbestos net. Agar coagulates at 40 ℃ and is usually not decomposed by microorganisms.
The content of agar in solid media varies with the quality of agar and the temperature.
Because this kind of media is mostly used to cultivate bacteria, it should be diluted with acid or alkali and adjust the PH to neutral or slightly alkaline to facilitate the growth and reproduction of bacteria.
 A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
 Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
 Microbiology Test in Food Industry
Microbiology Test in Food Industry
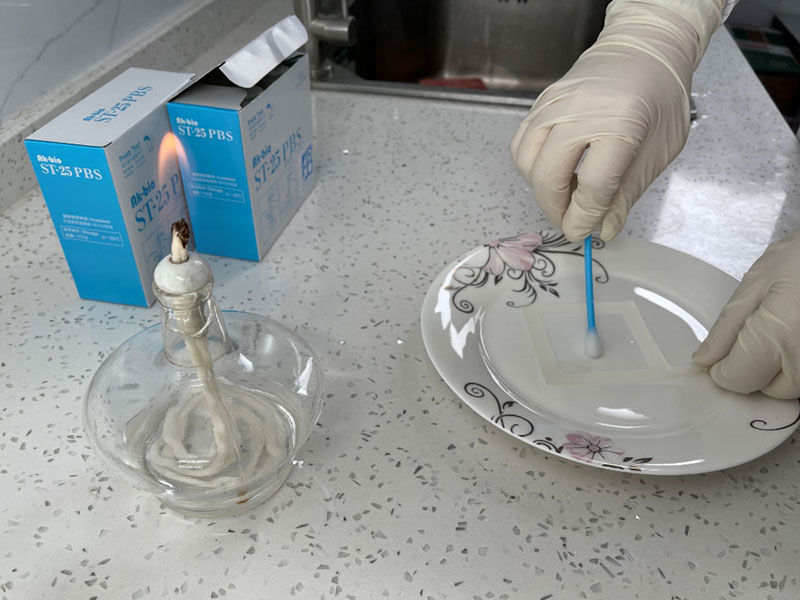 The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
 Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream
Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream

