Food microbiology exams are designed to assess students' understanding of critical concepts related to microorganisms in food, food safety practices, and laboratory techniques. These exams play a crucial role in ensuring that future food professionals have the necessary knowledge and skills to maintain food safety and quality. In this blog, we will explore some of the key topics that are often included in food microbiology exams.
Foodborne pathogens are microorganisms that can cause illness when consumed through contaminated food. Understanding common foodborne pathogens, their characteristics, sources, and control measures is essential for ensuring food safety. Microbial growth in food is influenced by various factors, including temperature, pH, water activity, and nutrient availability. Knowledge of microbial growth principles helps in predicting and preventing food spoilage and pathogen proliferation.
Food preservation methods aim to extend the shelf life of food products and inhibit microbial growth. Topics such as pasteurization, canning, freezing, and use of preservatives are important in understanding the principles of food preservation. Understanding the steps involved in investigating foodborne illness outbreaks is vital in identifying the source of contamination, preventing further cases, and implementing corrective measures to ensure food safety.
Laboratory techniques play a significant role in food microbiology exams. Topics may include aseptic handling, microbial isolation and identification, and techniques for quantifying microorganisms in food samples.
Food microbiology exams cover a wide range of critical topics related to microorganisms in food, food safety practices, and laboratory techniques. A comprehensive understanding of these key topics is crucial for students pursuing careers in the food industry, as it ensures they are equipped with the knowledge and skills to address food safety challenges effectively. By mastering these key topics, students can excel in their food microbiology exams and contribute to maintaining the safety and quality of the global food supply.
 A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
 Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
 Microbiology Test in Food Industry
Microbiology Test in Food Industry
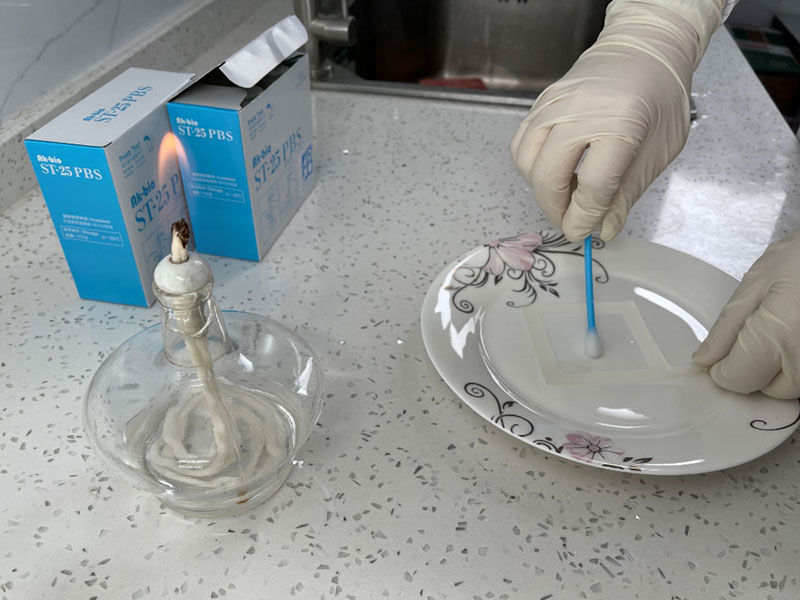 The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
 Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream
Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream


