1) Determine the sampling range according to the research purpose, disinfect and sterilize the sampling equipment in advance, and then take sampls;
2) Remove the floating soil on the surface, and use an ethanol-fired shovel to dig a 5-20cm underground soil layer;
3) After removing the visible impurities, the soil is passed through a 2mm screen, and each sample is collected and mixed from 3 or more sampling points, and each weighs 5 ~ 10g;
4) Store it in a sterile centrifuge tube and transported it below 0℃ back to the laboratory for DNA extraction;
5) If it cannot be extracted immediately, store it at -80°C.
1) The utensils should be disinfected and sterilized in advance. Collect rhizosphere soil from 20cm depth into a 50ml sterile tube;
2) Use a 20-mesh sieve to remove plant roots, animal remains and other impurities, and subpackage mirobiology samples into sterile centrifuge tubes, 3~5g each tube, and quickly store in liquid nitrogen;
3) Store at -80℃ immediately after sealing for later use.
1) Determine the sampling depth and scope according to the research purpose;
2) The collected water sample needs to be filtered through a filter membrane. The pore size of the filter membrane can be selected according to the turbidity of the water sample;
3) Store the filter membrane at -80°C for later use.
Note: For clear water samples, you can choose a small pore filter membrane, generally 0.22μm or 0.45μm filter membrane. The volume of the filtered water sample is more than 10L; the turbid water sample is allowed to stand for separating suspended particles before filtering, or pre-filter by a large filter membrane and then filter with a small one.
Activated sludge: Take 25mL of suspended activated sludge sample from the aeration tank and put it into an RNA-free tube, quickly put it in liquid nitrogen and transport it to the laboratory to extract DNA;
Surface sediments: Take the ground sediments from the ground surface of 0-10cm depth, put 1-2kg of sediments from each site into a sterile polyethylene plastic bag, and immediately place it at 0°C and transport it to the laboratory for DNA extraction.
1) Rinse the surface of the plant root sample with running water and pick out the small lateral roots. The clay soil particles should be chemically disinfected (95% sodium hypochlorite for 2 minutes);
2) Shake the glass beads violently in sterile water to physically remove bacteria;
3) Cut the root tissue with a scalpel blade to release endophytes;
4) Shake the sterile glass beads in 9% physiological saline for 4 hours at 30℃ to separate endophytes;
5) Filter with a 5μm membrane, centrifuge at 15000rpm, 4℃ to collect the precipitate and store in liquid nitrogen.
 A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
 Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
 Microbiology Test in Food Industry
Microbiology Test in Food Industry
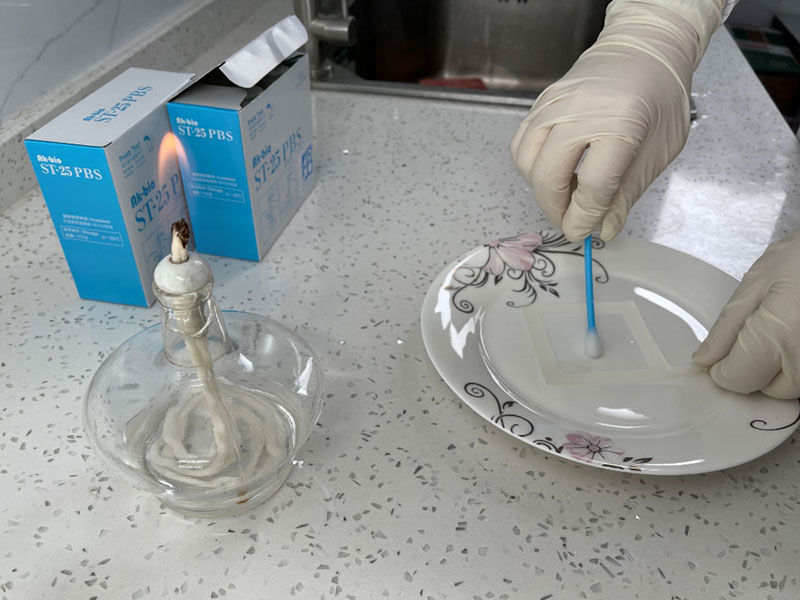 The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
 Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream
Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream


