According to the nutrient composition of the medium, it can be divided into following types of medium in microbiology laboratory: basic medium, complete medium and supplementary medium,etc. Such terms are mainly used in microbial genetics.
(1) Basic medium. It is also known as "minimum medium". It can only ensure the normal growth of wild-type strains of some microorganisms, and it is a synthetic medium with the lowest nutrient requirements, commonly expressed as "[-]". This kind of medium often lacks some growth factors, so the mutated nutrition deficient strain can not grow.
(2) Complete medium. If some natural substances (such as yeast extract, peptone, etc.) rich in chloro acid, vitamin and base are added to the basic medium, the growth factor is added to form a complete medium. Complete culture medium can be used to meet the growth needs of various nutrient deficient strains of microorganisms, often expressed as "[+]".
(3) Supplement medium. If one or several nutrients are added to the basic culture medium to meet the needs of the growth of the corresponding auxotrophic strains, this culture medium is called supplementary culture medium, which is commonly expressed as "[A]", "[B]".
Overall, in a microbiology laboratory, researchers can use three types of medium - basic, complete, and supplementary - according to the nutrient composition of the medium. Each medium has unique features that affect the growth and development of different types of microorganisms. Researchers should take into account the needs of various strains when selecting a suitable medium for their culture. By considering the characteristics of these three types of medium, researchers can design successful culture experiments to grow and analyze microbes to better understand their behavior and impact on various processes.
 A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
 Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
 Microbiology Test in Food Industry
Microbiology Test in Food Industry
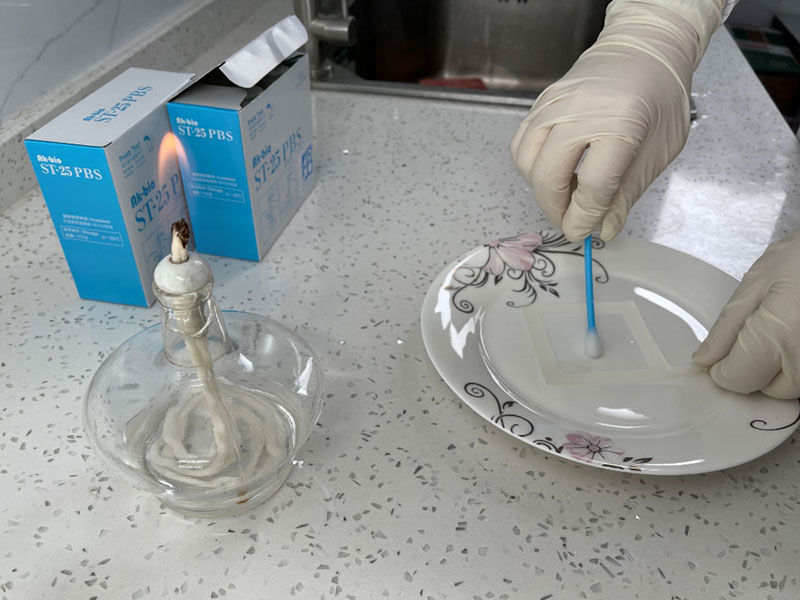 The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
 Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream
Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream