According to the purpose of the culture plates, they can be divided into cell culture plates and bacterial culture plates.
According to the manufacturing material, they are divided into plastic culture plates and glass culture plates, but most imported culture plates and disposable culture plates are made of plastic.
According to the size, they are usually divided into culture plates with diameters of 35mm, 60mm, 90mm, and 150mm.
According to the separation, they can be divided into two-segment culture plates, three-segment culture plates, etc.
The material of the culture plates is basically divided into two types, mainly plastic and glass, which are used for culturing various types of culture medium in microbiology. Glass can be used for plant materials, microbial culture, and animal cell adhesion culture. Plastics may be made of polyethylene, disposable or multiple-use, suitable for laboratory inoculation, line drawing, and separation of bacteria, and can be used for plant material culture.
During operation, the cover of the culture plate may be covered with water droplets or bacteria. Inverting the culture plate during culture can avoid water droplets or microorganisms on the surface of the culture plate.
During the culture process, bacteria will produce some metabolites that are harmful to bacterial growth, release heat, and discharge water. If the culture plate is not inverted, water droplets will drop into the culture medium, affecting the growth of bacterial colonies, thereby affecting the results of microbiology test in food industry or other industries.
Before use, the culture plate should be cleaned and disinfected. The cleanliness of the culture plate has a great impact on work, which can affect the acidity and alkalinity of the culture medium. If certain chemical reagents are present, they will inhibit bacterial growth.
Newly purchased culture plates should be rinsed with hot water and then soaked in a 1% or 2% hydrochloric acid solution for several hours to remove free alkaline substances, then rinsed twice with distilled water.
If you want to culture bacteria, use high-pressure steam (generally 6.8*10^5 Pa high-pressure steam), sterilize at 120℃ for 30 minutes, dry at room temperature, or use dry heat sterilization. Put the culture plate in the oven, maintain the temperature at around 120℃ for 2 hours, and kill the bacterial buds.
Only disinfected culture plates can be used for culturing.
 A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
A Tentative Study on the relevance of HACCP certification and infection control in hospital
 Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
Environmental Sanitation Microbiology Testing
 Microbiology Test in Food Industry
Microbiology Test in Food Industry
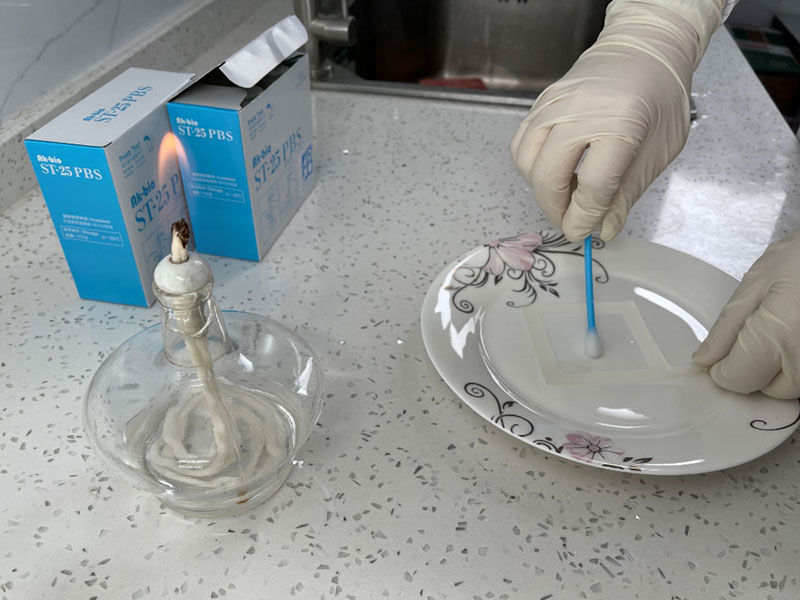 The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
The Applicability of High-quality Ready-to-use Swab Sampler for Tableware Sampling and Public Places Supplies and Utensils Microorganisms
 Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream
Spike Experiment of DNP Culture Media Plate Based on Ice Cream

